下载demo
克隆github项目
git clone git@github.com:Azure/DotNetty.git
阅读examples/Discard.Server工程,启动代码如下:
var bossGroup = new MultithreadEventLoopGroup(1);
var workerGroup = new MultithreadEventLoopGroup();
try
{
var bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap
.Group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.Channel<TcpServerSocketChannel>()
.Option(ChannelOption.SoBacklog, 100)
.Handler(new LoggingHandler("LSTN"))
.ChildHandler(new ActionChannelInitializer<ISocketChannel>(channel =>
{
IChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.Pipeline;
if (tlsCertificate != null)
{
pipeline.AddLast(TlsHandler.Server(tlsCertificate));
}
pipeline.AddLast(new LoggingHandler("CONN"));
pipeline.AddLast(new DiscardServerHandler());
}));
IChannel bootstrapChannel = await bootstrap.BindAsync(ServerSettings.Port);
Console.ReadLine();
await bootstrapChannel.CloseAsync();
}
finally
{
Task.WaitAll(bossGroup.ShutdownGracefullyAsync(), workerGroup.ShutdownGracefullyAsync());
}
ServerBootstrap
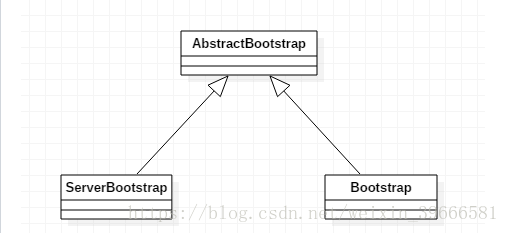 ServerBootstrap和Bootstrap都继承自AbstractBootstrap。
ServerBootstrap和Bootstrap都继承自AbstractBootstrap。
ServerBootstrap绑定到指定端口来监听客户端连接请求,Bootstrap连接至远程服务端。并且ServerBootstrap包含两个EventLoopGroup,而Bootstrap只包含一个EventLoopGroup。ServerBootstrap包含两组通道,第一组包含一个ServerChannel,表示服务器绑定到本地端口的监听套接字;第二组包含用来处理客户端连接所创建的所有通道,每接受一个连接时便会创建一个通道
Handler与ChildHandler
Handler方法由AbstractBootstrap提供,在初始化时执行
ChildHandler方法由ServerBootstrap提供,而ServerBootstrap继承自AbstractBootstrap,在客户端成功connect后才执行,目的是监听已经连接的客户端的Channel的动作和状态
AbstractBootstrap的小技巧
public abstract class AbstractBootstrap<TBootstrap, TChannel>
where TBootstrap : AbstractBootstrap<TBootstrap, TChannel>
where TChannel : IChannel
虚基类中定义的所有方法,都返回IBootstrap,如:
public virtual TBootstrap Group(IEventLoopGroup group)
{
Contract.Requires(group != null);
if (this.group != null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("group has already been set.");
}
this.group = group;
return (TBootstrap)this;
}
这样的好处,是让继承类的对象能同时调用虚基类方法和子类方法
var bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap
.Group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.Channel<TcpServerSocketChannel>()
.Option(ChannelOption.SoBacklog, 100)
.Handler(new LoggingHandler("LSTN"))
.ChildHandler(new ActionChannelInitializer<ISocketChannel>(channel =>
{
IChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.Pipeline;
if (tlsCertificate != null)
{
pipeline.AddLast(TlsHandler.Server(tlsCertificate));
}
pipeline.AddLast(new LoggingHandler("CONN"));
pipeline.AddLast(new NumberEncoder(), new BigIntegerDecoder(), new FactorialServerHandler());
}));
Group、Channel、Option、Handler都属于AbstractBootstrap提供的方法,ChildHandler由ServerBootstrap提供
这种技巧叫做Curiously recurring template pattern,参考知乎
Reactor模型
Reactor 模型是基于事件驱动的,有单线程模型、多线程模型和主从多线程模型:
单线程模型
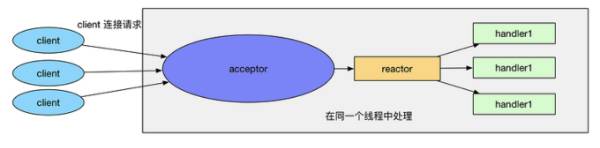 单线程模型指的是所有的 I/O 操作都是在同一个 NIO 线程上面完成, 由于 Reactor 模型使用的是 NIO,I/O 操作不会导致阻塞, 理论上一个线程可以独立处理所有 I/O 相关的操作
单线程模型指的是所有的 I/O 操作都是在同一个 NIO 线程上面完成, 由于 Reactor 模型使用的是 NIO,I/O 操作不会导致阻塞, 理论上一个线程可以独立处理所有 I/O 相关的操作
从架构层面看, 一个 NIO 线程确实可以完成其承担的职责, 例如通过 Acceptor 类接收客户端的 TCP 连接请求, 链路建立成功后通过 Dispatch 将对应的 ByteBuffer 派发到指定的 Handler 上进行消息处理并响应客户端
但一个 NIO 线程同时处理成百上千的链路, 性能上无法支撑, 即便 NIO 线程的 CPU 符合达到 100%, 也无法满足海量消息处理当负荷后处理速度变慢, 导致大量客户端连接超时, 最终导致大量消息积压和超时且一旦 NIO 线程发生故障则会导致整个通信模块不可用
var bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.Group( new MultithreadEventLoopGroup(1))
多线程模型
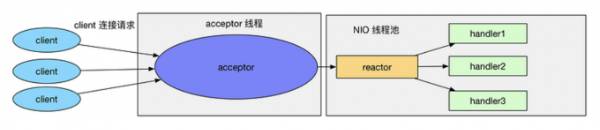 多线程模型与单线程模型最大区别就是有一组 NIO 线程处理 I/O 操作
多线程模型与单线程模型最大区别就是有一组 NIO 线程处理 I/O 操作
有专门一个 NIO 线程 (Acceptor) 用于接收客户端 TCP 连接请求, 读写 I/O 操作由一个 NIO 线程池负责
一个 NIO 线程可以同时处理 N 条链路, 但一个链路只对应一个 NIO 线程, 防止并发操作问题
var bossGroup = new MultithreadEventLoopGroup(1);
var workerGroup = new MultithreadEventLoopGroup();
var bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.Group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
主从多线程模型
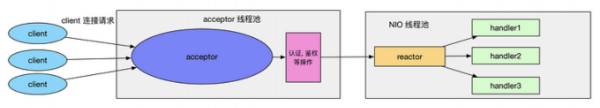 绝大多数场景下, 多线程模型都可以满足性能需求, 但是再极个别特殊场景中, 一个 NIO 线程处理客户端连接请求可能会存在性能问题, 例如百万客户端连接, 在这种情况下单独一个 Acceptor 线程可能会存在性能问题, 为了解决性能问题, 产生了主从多线程模型
绝大多数场景下, 多线程模型都可以满足性能需求, 但是再极个别特殊场景中, 一个 NIO 线程处理客户端连接请求可能会存在性能问题, 例如百万客户端连接, 在这种情况下单独一个 Acceptor 线程可能会存在性能问题, 为了解决性能问题, 产生了主从多线程模型
它的特点是: 服务端用于接收客户端连接的不再是单独一个 NIO 线程, 而是一个独立的 NIO 线程池
Acceptor 接收到客户端 TCP 连接请求处理完成后(可能包含接入认证等), 将新创建的 SocketChannel 注册到 I/O 线程池的某个线程上, 由它负责 SocketChannel 的读写和编解码工作
Acceptor 线程池仅仅只用于客户端的登陆握手和安全认证, 由 I/O 线程负责后续的 I/O 操作
DotNetty 没有使用主从多线程模型, 服务器端的 ServerSocketChannel 只绑定到了 bossGroup 中的一个线程, 因此在调用 Java NIO 的 Selector.select 处理客户端的连接请求时, 实际上是在一个线程中的, 所以对只有一个服务的应用来说, bossGroup 设置多个线程是没有什么作用的, 反而还会造成资源浪费
MultithreadEventLoopGroup
MultithreadEventLoopGroup是上节提到的线程池实现。包含一个IEventLoop数组,通过GetNext()方法顺序获取一个IEventLoop,对外提供IEventExecutor功能
public override IEventExecutor GetNext()
{
int id = Interlocked.Increment(ref this.requestId);
return this.eventLoops[Math.Abs(id % this.eventLoops.Length)];
}
上节例子中使用MultithreadEventLoopGroup,他有三种缺省参数的构造方法:
/// <summary>Creates a new instance of <see cref="MultithreadEventLoopGroup"/>.</summary>
public MultithreadEventLoopGroup()
: this(DefaultEventLoopFactory, DefaultEventLoopThreadCount)
{
}
/// <summary>Creates a new instance of <see cref="MultithreadEventLoopGroup"/>.</summary>
public MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int eventLoopCount)
: this(DefaultEventLoopFactory, eventLoopCount)
{
}
/// <summary>Creates a new instance of <see cref="MultithreadEventLoopGroup"/>.</summary>
public MultithreadEventLoopGroup(Func<IEventLoopGroup, IEventLoop> eventLoopFactory)
: this(eventLoopFactory, DefaultEventLoopThreadCount)
{
}
public MultithreadEventLoopGroup(Func<IEventLoopGroup, IEventLoop> eventLoopFactory, int eventLoopCount)
{
this.eventLoops = new IEventLoop[eventLoopCount];
var terminationTasks = new Task[eventLoopCount];
for (int i = 0; i < eventLoopCount; i++)
{
IEventLoop eventLoop;
bool success = false;
try
{
eventLoop = eventLoopFactory(this);
success = true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("failed to create a child event loop.", ex);
}
finally
{
// 如果创建失败,销毁之前的eventLoop
if (!success)
{
Task.WhenAll(
this.eventLoops
.Take(i)
.Select(loop => loop.ShutdownGracefullyAsync()))
.Wait();
}
}
this.eventLoops[i] = eventLoop;
terminationTasks[i] = eventLoop.TerminationCompletion;
}
this.TerminationCompletion = Task.WhenAll(terminationTasks);
}
缺省默认值:
static readonly int DefaultEventLoopThreadCount = Environment.ProcessorCount * 2;
static readonly Func<IEventLoopGroup, IEventLoop> DefaultEventLoopFactory = group => new SingleThreadEventLoop(group);
默认生成2倍cpu数量的线程
默认产生的IEventLoop的实现类为SingleThreadEventLoop
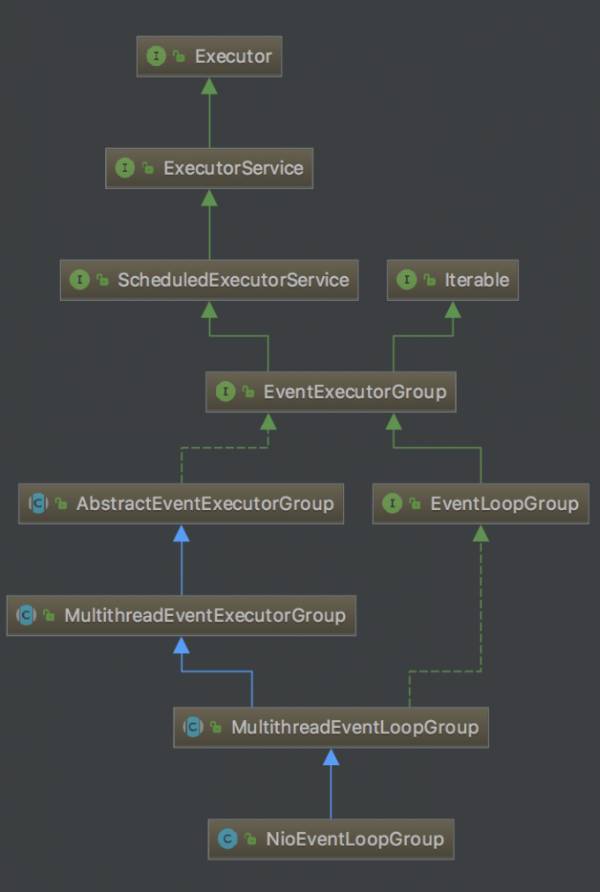
Dotnetty中没有NioEventLoopGroup类
这里要说明的是:
- MultithreadEventLoopGroup(IEventLoopGroup)是一个线程池,包含一个或多个SingleThreadEventLoop(IEventLoop)
- 一个SingleThreadEventLoop(IEventLoop)在它的生命周期内只和一个Thread绑定
- 所有 SingleThreadEventLoop(IEventLoop) 处理的 I/O 事件都将在它专有的 Thread 上被处理
- 一个 IChannel 在它的生命周期内只注册于一个 SingleThreadEventLoop(IEventLoop)
- 每一个 SingleThreadEventLoop(IEventLoop) 负责处理一个或多个 IChannel
SingleThreadEventLoop
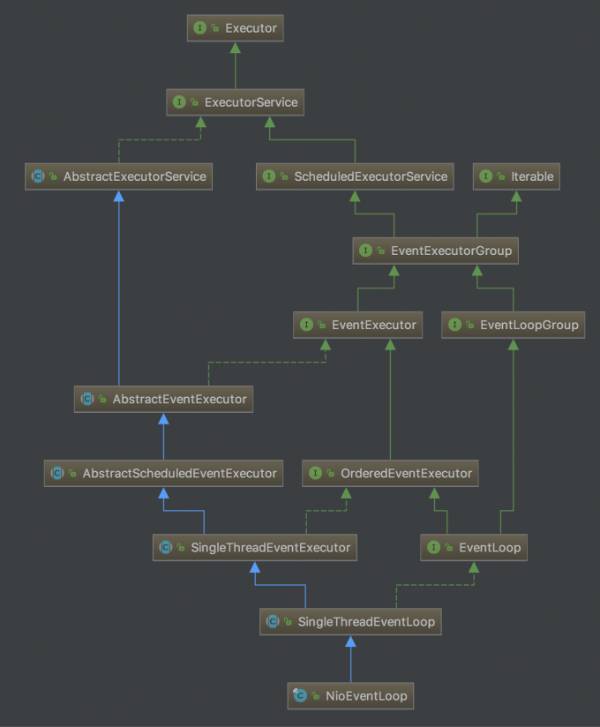 有点难以理解的是,IEventLoop继承自IEventLoopGroup!!!
有点难以理解的是,IEventLoop继承自IEventLoopGroup!!!
SingleThreadEventLoop是只有单个线程的线程池,但并不是一个纯粹的线程池,还负责处理系统 Task 和一些定时任务。
SingleThreadEventLoop继承自SingleThreadEventExecutor,调用父类的构造函数:
protected SingleThreadEventExecutor(IEventExecutorGroup parent, string threadName, TimeSpan breakoutInterval, IQueue<IRunnable> taskQueue)
: base(parent)
{
this.terminationCompletionSource = new TaskCompletionSource();
this.taskQueue = taskQueue;
this.preciseBreakoutInterval = PreciseTimeSpan.FromTimeSpan(breakoutInterval);
this.scheduler = new ExecutorTaskScheduler(this);
this.thread = new Thread(this.Loop);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(threadName))
{
this.thread.Name = DefaultWorkerThreadName;
}
else
{
this.thread.Name = threadName;
}
this.thread.Start();
}
其本质是声明了一个线程,执行Loop方法:
void Loop()
{
this.SetCurrentExecutor(this);
Task.Factory.StartNew(
() =>
{
try
{
Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref this.executionState, ST_STARTED, ST_NOT_STARTED);
while (!this.ConfirmShutdown())
{
this.RunAllTasks(this.preciseBreakoutInterval);
}
this.CleanupAndTerminate(true);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.Error("{}: execution loop failed", this.thread.Name, ex);
this.executionState = ST_TERMINATED;
this.terminationCompletionSource.TrySetException(ex);
}
},
CancellationToken.None,
TaskCreationOptions.None,
this.scheduler);
}
bool RunAllTasks(PreciseTimeSpan timeout)
{
this.FetchFromScheduledTaskQueue();
IRunnable task = this.PollTask();
if (task == null)
{
return false;
}
PreciseTimeSpan deadline = PreciseTimeSpan.Deadline(timeout);
long runTasks = 0;
PreciseTimeSpan executionTime;
while (true)
{
SafeExecute(task);
runTasks++;
// Check timeout every 64 tasks because nanoTime() is relatively expensive.
// XXX: Hard-coded value - will make it configurable if it is really a problem.
if ((runTasks & 0x3F) == 0)
{
executionTime = PreciseTimeSpan.FromStart;
if (executionTime >= deadline)
{
break;
}
}
task = this.PollTask();
if (task == null)
{
executionTime = PreciseTimeSpan.FromStart;
break;
}
}
this.lastExecutionTime = executionTime;
return true;
}
RunAllTasks取SingleThreadEventExecutor的taskQueue里的任务执行。
childGroup/workerGroup
ServerBootstrap的childGroup是如何起作用的?
IChannel boundChannel = await bootstrap.BindAsync(ServerSettings.Port);
从BindAsync一直跟进到ServerBootstrap的Init方法
protected override void Init(IChannel channel)
{
SetChannelOptions(channel, this.Options, Logger);
foreach (AttributeValue e in this.Attributes)
{
e.Set(channel);
}
IChannelPipeline p = channel.Pipeline;
IChannelHandler channelHandler = this.Handler();
if (channelHandler != null)
{
p.AddLast((string)null, channelHandler);
}
IEventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = this.childGroup;
IChannelHandler currentChildHandler = this.childHandler;
ChannelOptionValue[] currentChildOptions = this.childOptions.Values.ToArray();
AttributeValue[] currentChildAttrs = this.childAttrs.Values.ToArray();
p.AddLast(new ActionChannelInitializer<IChannel>(ch =>
{
ch.Pipeline.AddLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler,
currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}));
}
public sealed class ActionChannelInitializer<T> : ChannelInitializer<T>
where T : IChannel
{
readonly Action<T> initializationAction;
public ActionChannelInitializer(Action<T> initializationAction)
{
Contract.Requires(initializationAction != null);
this.initializationAction = initializationAction;
}
protected override void InitChannel(T channel) => this.initializationAction(channel);
public override string ToString() => nameof(ActionChannelInitializer<T>) + "[" + StringUtil.SimpleClassName(typeof(T)) + "]";
}
负责accept新链接的channel的pipeline添加了ActionChannelInitializer,来看ActionChannelInitializer的InitChannel方法说明:
This method will be called once the IChannel was registered. After the method returns this instance will be removed from the IChannelPipeline of the IChannel.
其目的是在IChannel被register到IEventLoop的时候执行,然后从IChannel的pipeline中移除自己。
来看看ServerBootstrapAcceptor的代码:
public override void ChannelRead(IChannelHandlerContext ctx, object msg)
{
var child = (IChannel)msg;
child.Pipeline.AddLast((string)null, this.childHandler);
SetChannelOptions(child, this.childOptions, Logger);
foreach (AttributeValue attr in this.childAttrs)
{
attr.Set(child);
}
// todo: async/await instead?
try
{
this.childGroup.RegisterAsync(child).ContinueWith(
(future, state) => ForceClose((IChannel)state, future.Exception),
child,
TaskContinuationOptions.NotOnRanToCompletion | TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ForceClose(child, ex);
}
}
当IChannel可读时,把IChannel绑定到childGroup的一个IEventLoop上去。
来看看this.childGroup.RegisterAsync(child)的实现:
public override IEventExecutor GetNext()
{
int id = Interlocked.Increment(ref this.requestId);
return this.eventLoops[Math.Abs(id % this.eventLoops.Length)];
}
public Task RegisterAsync(IChannel channel) => ((IEventLoop)this.GetNext()).RegisterAsync(channel);
MultithreadEventLoopGroup按顺序选择一个SingleThreadEventLoop,绑定此IChannel。
pipeline、context与handler之间的关系
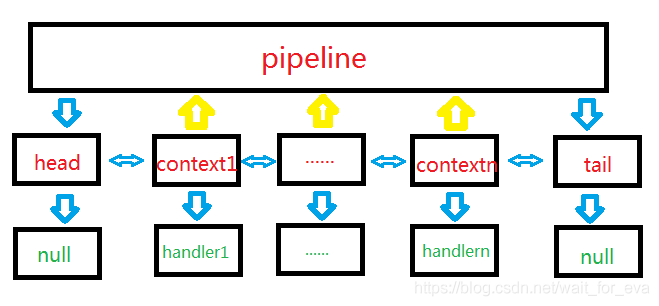
- 每个handler都是无关联的
- handler都是伴生于context的
- context是伴生于一个双线链表当中
- 双向链表伴生于pipeline
- context中保留有pipeline的引用
handler
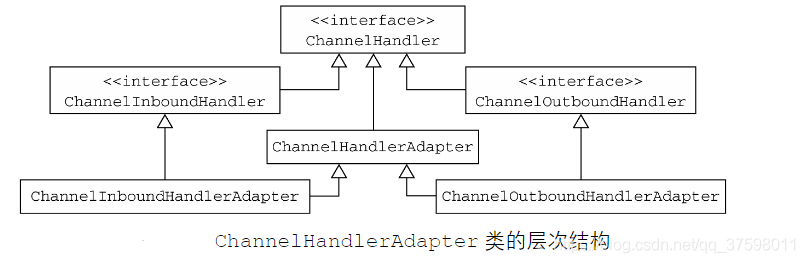 这是netty中的类图,DotNetty中去掉了ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter和ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter,所有的Handler继承自->ChannelHandlerAdapter->IChannelHandler
这是netty中的类图,DotNetty中去掉了ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter和ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter,所有的Handler继承自->ChannelHandlerAdapter->IChannelHandler